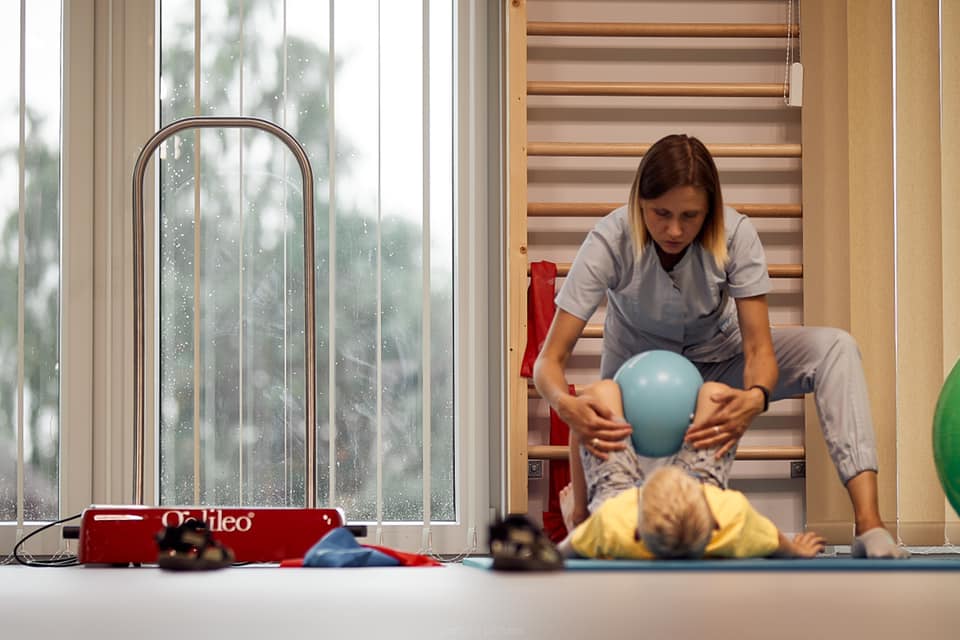
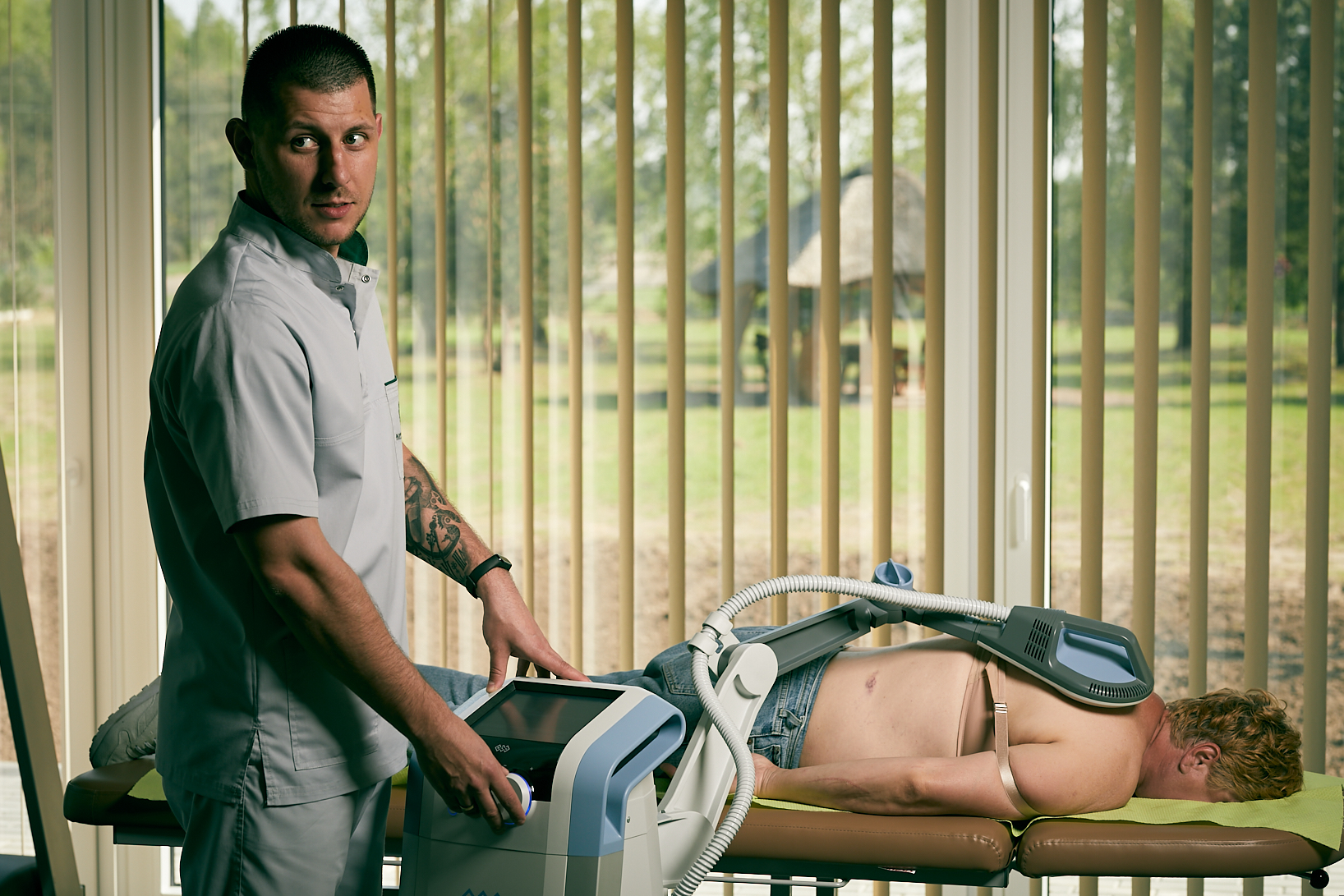
Shockwave is a new treatment used in the rehabilitation of musculoskeletal disorders.
It is defined as a periodic fluctuation of pressure that dissipates very quickly in space. The shock wave is characterized by an extremely rapid increase in pressure amplitude: 50-100 MPa. Such a value is assigned to its front part. The period of the aforementioned increase is relatively short and is less than 10 ns. This is followed by a decrease in its value over a period of 1 μs, which is maintained at a uniform level of nearly 10 μs.
The result of shock wave therapy is an analgesic effect, acceleration of tissue regeneration processes, intensification of collagen synthesis and the process of angiogenesis, i.e. creation of new blood vessels. The branch of physiotherapy that uses shock wave is physical therapy.
Shockwave in physiotherapy - what is the treatment?
Shockwave treatments involve the use of a special device that emits waves. After taking a history, analyzing any imaging results and determining the greatest tenderness, the appropriate parameters are set and the treatment begins. A gel is applied to the shock wave emitting head, and then applied directly to the affected area on the body. During the therapy, pain may occur; its intensity depends on the parameters used, the patient’s problem and what the nature of the condition is.
Indications for use (blue filter)
- skin irritation,
- dry and sensitive skin,
- epidermal exfoliation,
- frostbite,
- dilated blood vessels,
- Trigeminal neuralgia,
- Occipital neuralgia,
- sciatica,
- scabies,
- psoriasis,
- Painful menstruation (after bleeding has stopped),
- dilated blood vessels,
- Raynaud's disease.
In order to use Sollux lamps safely, it is necessary to remember the contraindications to the use of treatments with it.
Contraindications to use:
- febrile states,
- generalized infection,
- Active pulmonary tuberculosis,
- circulatory insufficiency,
- Predisposition to bleeding,
- general states of cachexia,
- Acute inflammation of both skin and soft tissues,
- trophic changes,
- arteriosclerosis,
- swelling,
- sensory disturbances,
- cancers,
- hypertension,
- pregnancy,
- states after a heart attack,
- hyperthyroidism.
It is necessary to follow the described safety rules, especially when using the sollux lamp at home due to the possibility of dangerous complications, which are:
- heat stroke,
- Io, IIo ,IIIo burns,
- vision damage,
- Adverse vascular reaction (cyanosis).